In the modern-day world, almost everything that is required is happening just with a few touches with our fingertips without going anywhere. Thanks to the internet technologies and services that are built on top of them. Let's explore one of the primitive yet a very powerful tool to date i.e browser. Let's rip it into pieces and understand how that works.
It's a software application which is used to access WorldWideWeb.
Its purpose is to fetch the content from a server and renders it on the user device.
Components of a browser
The key parts of a browser are listed below.
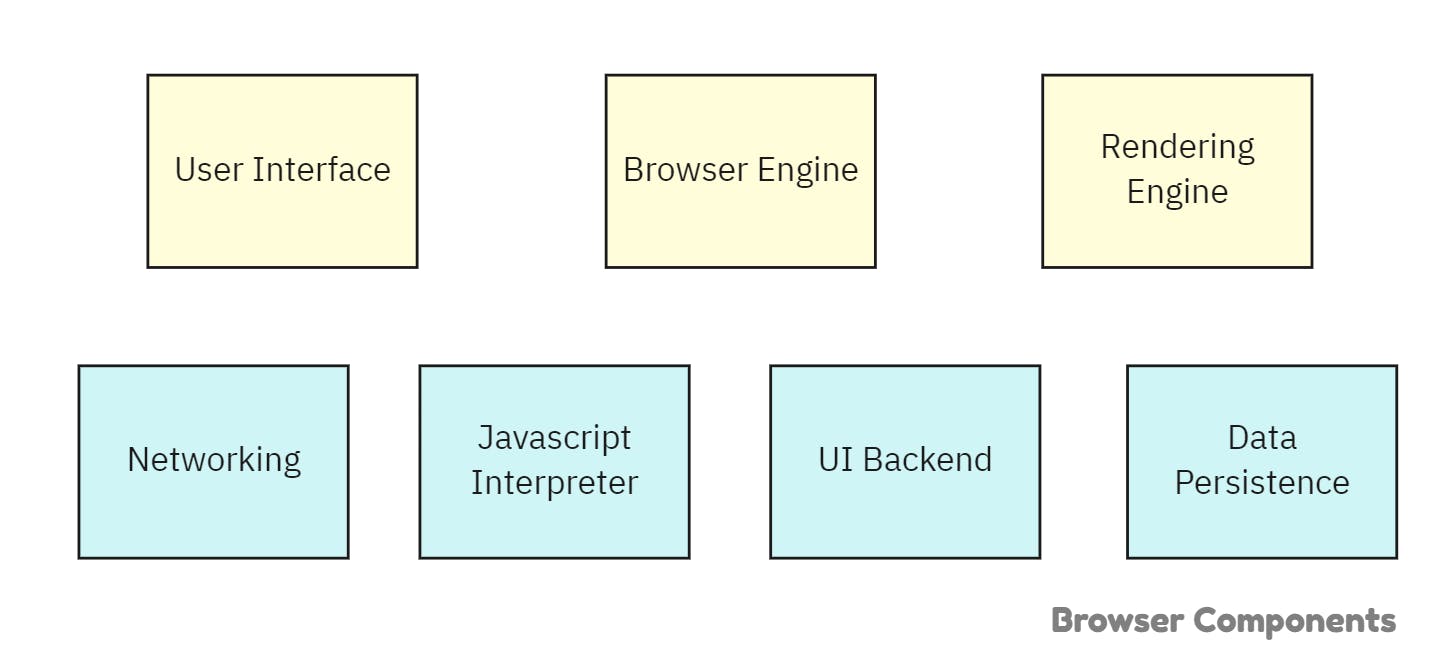
- User Interface
- It the entire visible part of a browser which comprises the address bar, forward & backward button, bookmarking menu, etc. It is every other part of the browser except the rendering or paint area (the Area where a web page gets drawn).
- Browser engine
- It works as a translator between Browser UI and rendering engine.
- It maps the user inputs and interactions to appropriate functions in the rendering engine.
- Eg: The click of a back button on UI should trigger the render of the previous page. So, this intimation to render engine is handled by browser engine.
- Rendering Engine
- It is responsible to render the requested webpage on to browser screen.
- Every browser has its own rendering engine. Safari uses WebKit, Firefox uses Gecko & Chrome uses Blink (forked version of WebKit).
- Networking
- It takes care of retrieving the data from the urls with the help of standard internet protocols like HTTP, FTP & SMTP etc. It also handles all the aspects of security and internet communication.
- JS Interpreter
- It is responsible to parse and execute the javascript code present in the website. The final output is sent to the rendering engine for painting it.
- Chrome uses V8 engine, Firefox uses SpiderMonkey and Edge uses Chakra Javascript engines.
- UI Backend
- UI backend is used for drawing basic widgets; such as a select box, input box, check box, and windows.
- It is a backend that exposes a generic interface that is not platform specific & internally uses operating system user interface methods.
- Usually, operating systems have GUI (Graphical user interfaces) & TUI (Text user interface).
- Eg: The checkbox or list of the same website is rendered differently in iOS, windows & android.
- Data Persistence
- Browsers need a place to store the data locally.
- Eg: Personalizing site preferences (displaying a user's choice of custom widgets, colour scheme, & font size etc.)
- There are various storage options available. Local storage, Session Storage, Cookies, WebSQL, IndexedDB, & FileSystem are namely a few.
Workflow
Let's go into a simple workflow of rendering an HTML page.
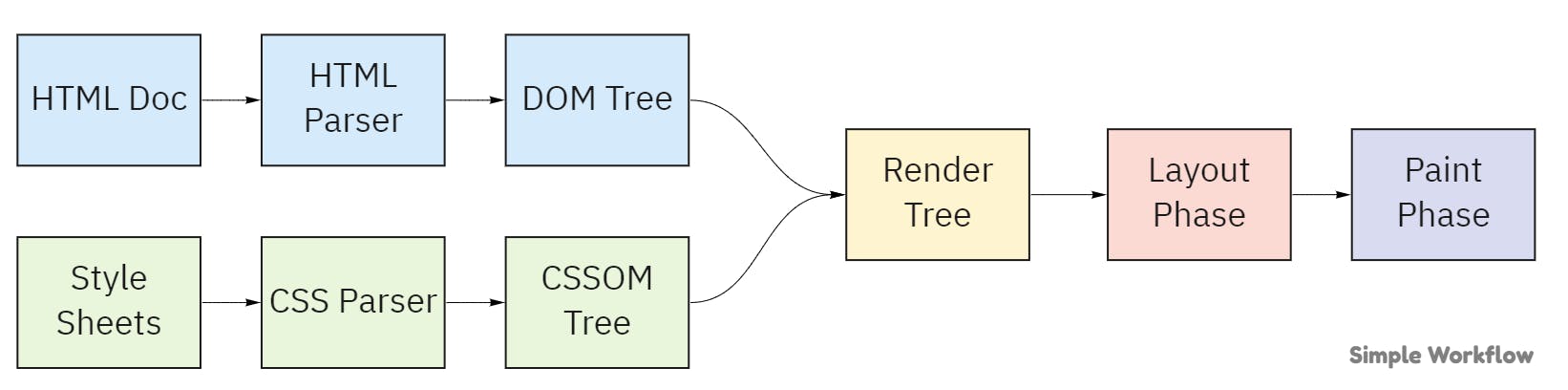
- The HTML file and CSS files fetched from the network layer are sent to respective parsers.
- The HTML parser will parse the HTML document and will convert it into a tree of nodes called a DOM (Document Object Model) Tree.
- CSS parser converts the CSS properties of a tag or node into a browser understandable code and will create a CSSOM (Cascading Style Sheet Object Model) Tree.
- Finally, these two are utilized to create the final Render Tree.
- Browser by looking at the render tree and metadata of nodes will create a layout with exact dimensions and co-ordinates where each HTML element along with its styles should appear.
- Paint phase converts each node of the render tree to the pixels on the screen.
HTML to DOM Tree
- The HTML code will be converted to DOM by a parser. A simple visual representation is shown below.
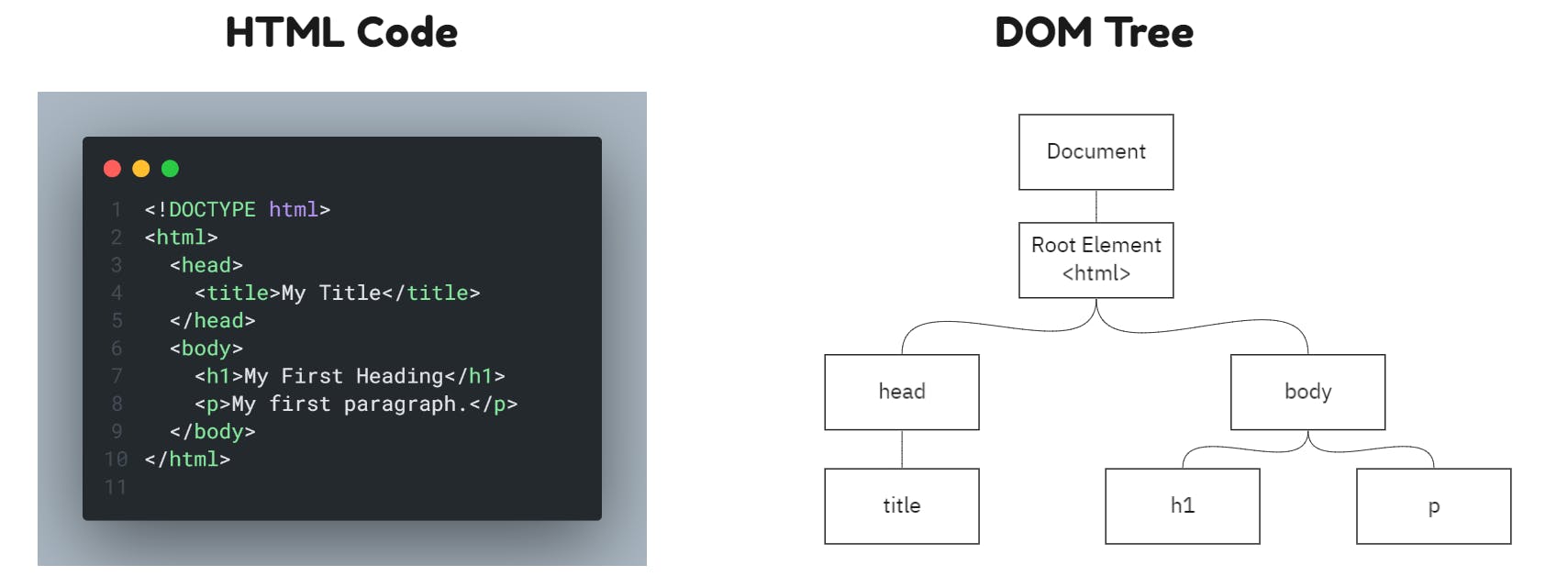
- In the DOM tree each element is represented as a node.
- It starts with HTML as the root node and will go on building it as the elements appear to the parsing engine.
- Below is the diagram that shows how to find everything in a browser.
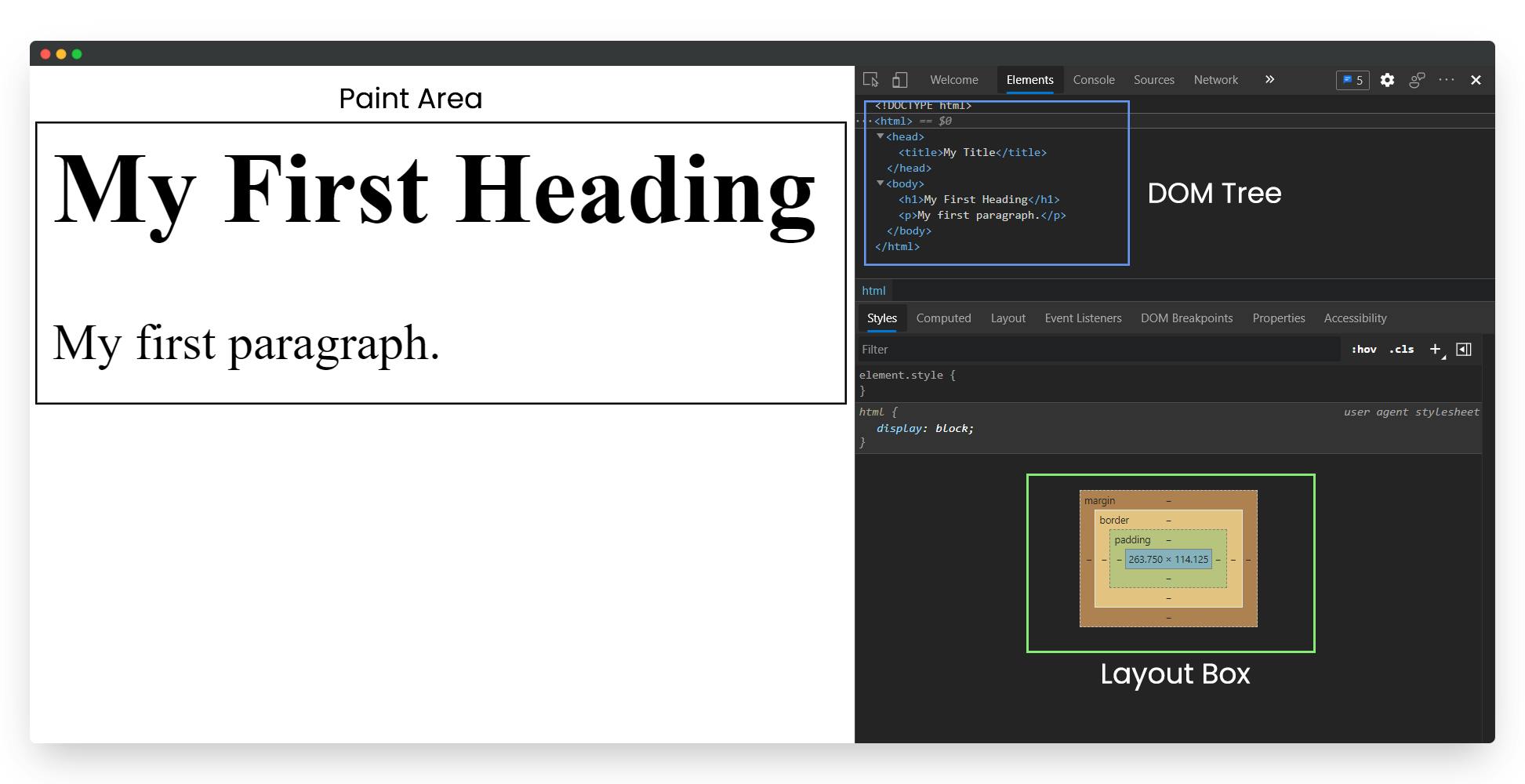
So, that ends our brief explanation about the browser and its internal workings.
References & Useful Links 🔗
- https://hackernoon.com/how-do-web-browsers-work-40cefd2cb1e1
- https://www.html5rocks.com/en/tutorials/internals/howbrowserswork/?ref=hackernoon.com
- https://www.browserstack.com/guide/browser-rendering-engine#:~:text=Rendering Engine%3A As the name,displayed on the user interface.
- https://blogs.helsinki.fi/students-digital-skills/1-introduction-to-the-use-of-computers/1-1-computer-functionality/operating-system-and-user-interface/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RVnARGhhs9w
- https://medium.com/weekly-webtips/understand-dom-cssom-render-tree-layout-and-painting-9f002f43d1aa

